AQA Computer Science GCSE
This page is up to date for the AQA 8525 syllabus for exams from 2022.
Computer Systems - Fetch–Decode–Execute Cycle
The CPU processes data. To do that it needs to move data and instructions around the computer system - using buses to move things stored in RAM into and out of the CPU's registers.
The ways it does this can be simplified down to the Fetch–Decode–Execute cycle.
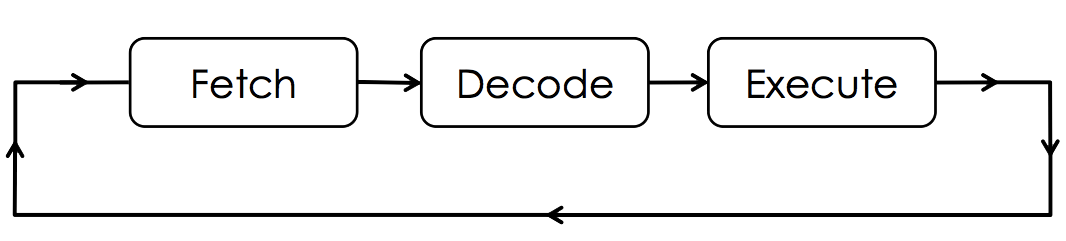
![]() Fetch–Decode–Execute - slides from class
Fetch–Decode–Execute - slides from class
The Fetch–Decode–Execute cycle is managed by the Control Unit element of the CPU. It involves the movement of data into and out of the CPU from main memory (RAM).
